Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory on Luminescence and Optical Information Technology, Ministry of Education, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
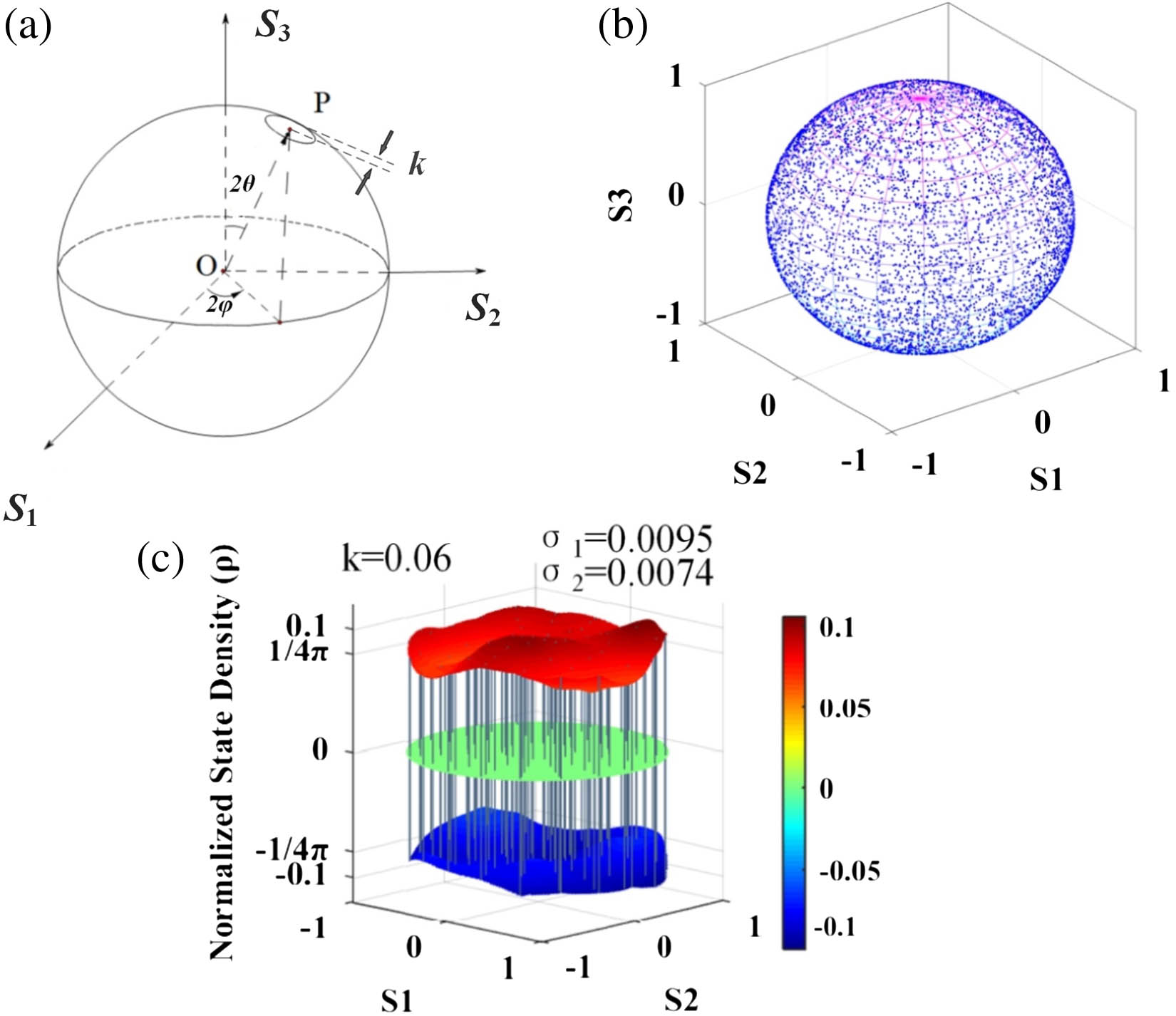
We report a new method to deeply analyze the scrambling characteristic of polarization scramblers based on density of polarization states (DPS) statistics that makes it possible to describe the DPS distribution in detail on the whole Poincaré sphere, thus easy to locate accurately the nonuniform areas of defective polarization scramblers, which cannot be realized by existing methods. We have built a polarization scrambling system to demonstrate the advantages of our method compared with others by experiments and suggested effective evaluation indexes whose validity is well confirmed by applying to a commercial scrambler. Our conclusions are valuable for accurately analyzing and diagnosing the performance of any polarization scrambler, and quality evaluation of polarization controllers or other polarization devices.
optical communication polarization scrambling density of polarization states Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(6): 060604

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Luminescence and Optical Information Technology, Ministry of Education, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
We propose and demonstrate a novel scheme of semi-open-loop polarization control (SOL-PC), which controls the state of polarization (SOP) with high accuracy and uniform high speed. For any desired SOP, we first adjust the initial SOP using open-loop control (OLC) based on the matrix model of a three-unit piezoelectric polarization controller, and quickly move it close to the objective one. Then closed-loop control (CLC) is performed to reduce the error and reach precisely the desired SOP. The response time is three orders faster than that of the present closed-loop polarization control, while the average deviation is on par with it. Finally, the SOL-PC system is successfully applied to realize the suppression of the polarization mode dispersion (PMD) effect and reduce the first-order PMD to near zero. Due to its perfect performance, the SOL-PC energizes the present polarization control to pursue an ideal product that can meet the future requirements in ultrafast optical transmission and quantum communication.
polarization control polarization mode dispersion fiber optics components coherent communications Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(5): 050601

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 e-mail: ypwang@szu.edu.cn
A liquid modified photonic crystal fiber (PCF) integrated with an embedded directional coupler and multi-mode interferometer is fabricated by infiltrating three adjacent air holes of the innermost layer with standard 1.48 refractive index liquids. The refractive index of the filled liquid is higher than that of background silica, which can not only support the transmitting rod modes but also the “liquid modified core” modes propagating between the PCF core and the liquid rods. Hence, the light propagating in the liquid modified core can be efficiently coupled into the satellite waveguides under the phase-matching conditions, resulting in a dramatic decrease of the resonant wavelength intensity. Furthermore, there is a multi-mode interference produced by modified core modes and rod modes. Such a compact (~0.91 cm) device integrated with an embedded coupler and interferometer is demonstrated for high-sensitivity simultaneous temperature (~14.72 nm/°C) and strain (~13.01 pm/μ ) measurement.
Micro-optical devices Fiber optics sensors Photonic crystal fibers Photonics Research
2017, 5(2): 02000129

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Lab of Education Ministry on Luminescence and Optical Information Technology, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
2 The Institute of Optics, University of Rochester, 275 Hutchison Road, Rochester, New York 14627, USA
We demonstrate an ultralow-noise single-photon detection system based on a sensitive photomultiplier tube (PMT) with precise temperature control, which can capture fast single photons with intervals around 10 ns. By improvement of the electromagnetic shielding and introduction of the self-differencing method, the dark counts (DCs) are cut down to ~1%. We further develop an ultra-stable PMT cooling subsystem and observe that the DC goes down by a factor of 3.9 each time the temperature drops 10°C. At 20°C it is reduced 400 times with respect to the room temperature (25°C), that is, it becomes only 2 counts per second, which is on par with the superconducting nanowire detectors. Meanwhile, despite a 50% loss, the detection efficiency is still 13%. Our detector is available for ultra-precise single-photon detection in environments with strong electromagnetic disturbances.
030.5260 Photon counting Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(10): 100301
北京交通大学 发光与光信息技术教育部重点实验室, 北京100044
随着光学操控技术的迅速发展, 测量与重建径向偏振光束(RPB)成为迫切任务之一。利用一套石英旋光片组合, 首先产生了RPB。借助计算机控制的CCD, 对RPB的斯托克斯矢量场分布进行了测量, 并获得其偏振态分布。结果表明: 所产生的RPB归一化功率偏差为0.054 8, 偏振偏差为0.004 4。利用干涉仪, 获得了RPB的相位分布, 相邻断面间平均相位差为1.471。最后, 通过偏振和相位信息的数据处理, 成功重建了RPB的矢量场分布, 并发现其拓扑荷在3左右。这些结论为实现精密量子调控与测量铺平了道路。
径向偏振光束 斯托克斯矢量 干涉仪 光场重建 radially polarized beams Stokes vector interferometer optical field reconstructing 红外与激光工程
2017, 46(4): 0427002

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Education Ministry on Luminescence and Optical Information Technology, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
2 Institute of Optical Information, School of Science, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
Polarization-based optical communications are attracting more attention recently, where the crucial points are polarization features and their measurements. Based on the Müller matrix method, we obtain measurable expressions for the polarization-dependent gain (PDG) and the loss of polarization orthogonality (LPO), while give the boundary of the LPO for any PDG devices. We experimentally demonstrate that non-linear LPO can be created in a semiconductor optical amplifier and find that the LPO will slightly skim over the boundary near the threshold of the injected current. Furthermore, an empirical formula is achieved to gauge the LPO-induced power penalty, which is proven to be valid in differential polarization shift-keying transmission by executing a bit error rate measurement. Our conclusions are applicable to non-orthogonal polarization cases and valuable to polarization-related communications, even orbital angular momentum multiplexing.
060.2330 Fiber optics communications 260.5430 Polarization 060.2340 Fiber optics components Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(9): 090601
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 e-mail: cliao@szu.edu.cn
3 School of Information Science and Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
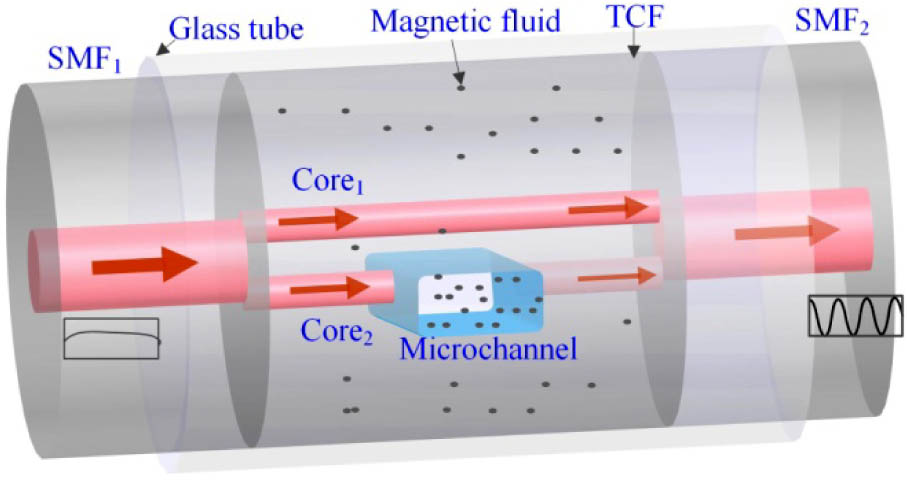
An ultrasensitive magnetic field sensor based on a compact in-fiber Mach–Zehnder interferometer (MZI) created in twin-core fiber (TCF) is proposed, and its performance is experimentally demonstrated. A section of TCF was spliced between two sections of standard single-mode fibers, and then a microchannel was drilled throughone core of the TCF by means of femtosecond laser micromachining. The TCF with one microchannel was then immersed in a water-based Fe3O4 magnetic fluid (MF), forming a direct component of the light propagation path, and then sealed in a capillary tube, achieving a magnetic sensing element, which merges the advantages of an MZI with an MF. Experiments were conducted to investigate the magnetic response of the proposed sensor. The developed magnetic field sensor exhibits a linear response within a measurement range from 5 to 9.5 mT and an ultrahigh sensitivity of 20.8 nm/mT, which, to our best knowledge, is 2 orders of magnitude greater than other previously reported magnetic sensors. The proposed sensor is expected to offer significant potential for detecting weak magnetic fields.
Interference Interference Microstructured fibers Microstructured fibers Fiber optics sensors Fiber optics sensors Photonics Research
2016, 4(5): 05000197
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Luminescence and Optical Information, Ministry of Education, Institute of Optical Information, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
Quasi-single-photon sources are attracting a lot of interest in many fields at present; however, the knowledge is very poor about their performance. In this Letter, by using the standard Hanbury-Brown-Twiss measurement method, we investigate in detail the characteristics of the photons from an attenuated continuous single-mode red laser. For the first time to our knowledge we obtain the coincidence counting spectrum of a commercial single-photon source, which demonstrates that an appropriately attenuated continuous laser can be utilized as a quasi-single-photon source for general applications.
Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(Suppl): S20301
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Luminescence and Optical Information of Ministry of Education, and Institute of Optical Information, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
Based on elasto-optic effect theory, we present a simplified model for the fiber squeezer assisted with a piezoceramic actuator (PZT), and it is experimentally demonstrated with reasonable approximation. Results show that there is a quadratic polynomial relationship between the arccosine reciprocal value of light intensity outputted from polarization analyzer and the reciprocal value of applied voltage for the PZT. Using this formula, the key parameters of the PZT such as the piezoelectric strain coefficient are further obtained. Our conclusions are significant for accurate measurement and polarization control.
060.2310 Fiber optics 260.1440 Birefringence 260.5430 Polarization Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(s2): S20602
1 北京交通大学发光与光信息技术教育部重点实验室, 北京 100044
2 北京交通大学理学院光信息科学与技术研究所, 北京 100044
3 重庆光电技术研究所, 重庆 400060
偏振编码器的稳定性是影响偏振编码通信的关键因素之一。采用时变矢量对基于铌酸锂(LN)相位调制的偏振编码器的稳定性进行了深入研究。实验表明,LN的偏振相关损耗主态(PPL)与偏振相关相移主态基本一致,说明LN的偏振相关损耗不会影响偏振态的稳定性。实验中观察到偏振态旋转具有“惯性”:使电压从0增加到某个定值,在停止增加后,偏振态会继续变化一段时间,大约在30 min后才达到稳定;相反,使电压从某个定值减少为0,在停止减少后,偏振态仍会继续变化一段时间。该现象对于低速调制将带来不利影响;对于高速调制,平均功率的变化也将引起偏振抖动。
光纤光学 光纤器件 偏振编码通信 偏振编码器 稳定性





